ngnix mTLS Ingress
Mutual TLS, or mTLS for short, is a method for mutual authentication. mTLS ensures that the parties at each end of a network connection are who they claim to be by verifying that they both have the correct private key. The information within their respective TLS certificates provides additional verification .mTLS is often used in a Zero Trust security framework* to verify users, devices, and servers within an organization. It can also help keep APIs secure.
In mTLS, however, both the client and server have a certificate, and both sides authenticate using their public/private key pair. Compared to regular TLS, there are additional steps in mTLS to verify both parties (additional steps in bold):
- Client connects to server.
- Server presents its TLS server.
- Client vertifies server's certificates.
- Client presents its TLS certificate.
- Server verifies its client's certificate.
- Server grants access.
- Client and server exchange information over encrypted TLS connection
Certificate authority in mTLS
The organization implementing mTLS acts as its own certificate authority. This contrasts with standard TLS, in which the certificate authority is an external organization that checks if the certificate owner legitimately owns the associated domain (learn about TLS certificate validation).
A "root" TLS certificate is necessary for mTLS; this enables an organization to be their own certificate authority. The certificates used by authorized clients and servers have to correspond to this root certificate. The root certificate is self-signed, meaning that the organization creates it themselves.
TLS 1.2 vs TLS 1.3
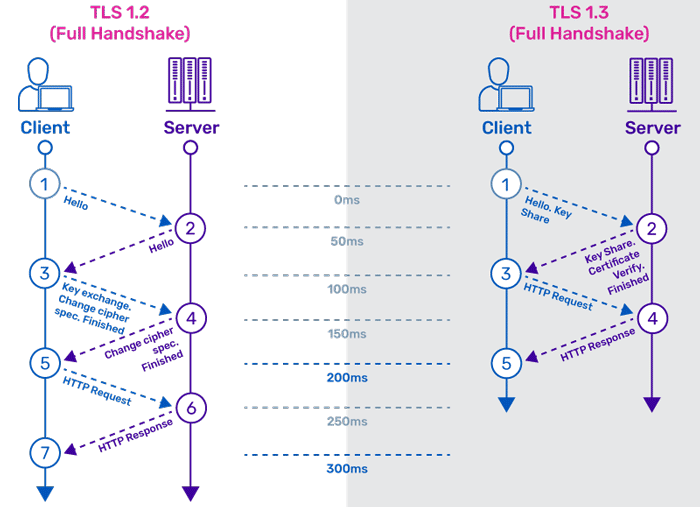
TLS and mTLS Comparison
TLS handshake
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Client hello (1):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Server hello (2):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Certificate (11):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Server key exchange (12):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Server finished (14):
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Client key exchange (16):
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS change cipher, Client hello (1):
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Finished (20):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS change cipher, Client hello (1):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Finished (20):
mTLS handshake
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Client hello (1):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Server hello (2):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Certificate (11):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Server key exchange (12):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Request CERT (13):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Server finished (14):
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Certificate (11):
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Client key exchange (16):
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS change cipher, Client hello (1):
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Finished (20):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS change cipher, Client hello (1):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Finished (20):
Ingress Setup in nginx ingress
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: httpbin
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: ca-issuer
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-tls-verify-client: "on"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-tls-secret: "ingress-nginx/logpoint-ingress"
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
- in.logpoint.com.np
secretName: logpoint-ingress
rules:
- host: in.logpoint.com.np
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: httpbin
servicePort: 8000
path: /
client mTLS certificate generation
{
"CN":"roshankhatri",
"key":{
"algo":"rsa",
"size":2048
},
"names":[
{
"C":"NP",
"L":"Lalitpur",
"O":"Logpoint Nepal",
"OU":"ITOps",
"ST":"Nepal"
}
],
"hosts":[
""
]
}
Generate certificate & Convert to PKCS12 format
Generate certificate using intermediate certificate authority
cfssl gencert -ca intermediate_ca.pem -ca-key intermediate_ca-key.pem -config profile.json --profile=client roshankhatri.json | cfssljson -bare roshankhatri
View generated certificate using openssl
Convert to PKCS12 format & append certificate chain
openssl pkcs12 -export -inkey roshankhatri-key.pem -in roshankhatri.pem -certfile merobundle.pem -out roshankhatri.p12
View info about PKCS12 Certificate
Import mTLS Certificate into keychain mac
Open keychain > System > My Certificates - Import p12 certificates
On Firefox Import p12 certificate and root certificate